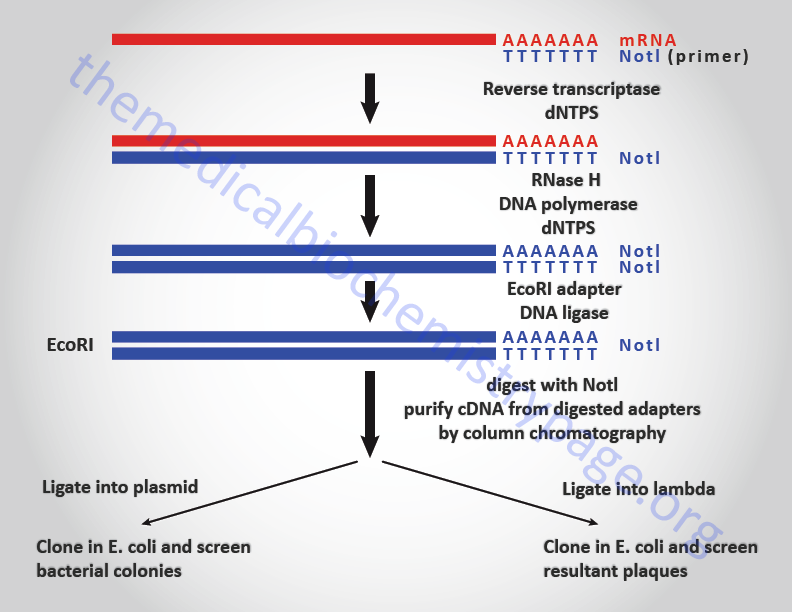
What Is Cdna Cloning . Unlike genomic dna clones, cdna clones lack intron sequences, making them the clones of choice for analyzing the protein product of a gene. Construction of cdna clones involves the synthesis of complementary dna from mrna and then. In molecular cloning, dna library construction refers to the creation of clones that carry dna fragments representing the complete genomic. The cloning of expressed genes and the polymerase chain reaction (pcr), two biotechnological breakthroughs of the 1970s and 1980s, continue to play. Cdna cloning is one of the fundamental technologies in molecular biology, and most of our knowledge about transcripts and proteins is. Cdna (short for copy dna; Also called complementary dna) is synthetic dna that has been transcribed from a specific mrna through a reaction using the enzyme reverse. Cdna clones are copies of mrnas.
from themedicalbiochemistrypage.org
Construction of cdna clones involves the synthesis of complementary dna from mrna and then. Cdna clones are copies of mrnas. Cdna cloning is one of the fundamental technologies in molecular biology, and most of our knowledge about transcripts and proteins is. Cdna (short for copy dna; Also called complementary dna) is synthetic dna that has been transcribed from a specific mrna through a reaction using the enzyme reverse. The cloning of expressed genes and the polymerase chain reaction (pcr), two biotechnological breakthroughs of the 1970s and 1980s, continue to play. In molecular cloning, dna library construction refers to the creation of clones that carry dna fragments representing the complete genomic. Unlike genomic dna clones, cdna clones lack intron sequences, making them the clones of choice for analyzing the protein product of a gene.
Molecular Biology in Medicine The Medical Biochemistry Page
What Is Cdna Cloning Unlike genomic dna clones, cdna clones lack intron sequences, making them the clones of choice for analyzing the protein product of a gene. Cdna (short for copy dna; Also called complementary dna) is synthetic dna that has been transcribed from a specific mrna through a reaction using the enzyme reverse. Cdna clones are copies of mrnas. Cdna cloning is one of the fundamental technologies in molecular biology, and most of our knowledge about transcripts and proteins is. Construction of cdna clones involves the synthesis of complementary dna from mrna and then. In molecular cloning, dna library construction refers to the creation of clones that carry dna fragments representing the complete genomic. The cloning of expressed genes and the polymerase chain reaction (pcr), two biotechnological breakthroughs of the 1970s and 1980s, continue to play. Unlike genomic dna clones, cdna clones lack intron sequences, making them the clones of choice for analyzing the protein product of a gene.
From courses.lumenlearning.com
Cloning Biology for Majors I What Is Cdna Cloning Cdna clones are copies of mrnas. The cloning of expressed genes and the polymerase chain reaction (pcr), two biotechnological breakthroughs of the 1970s and 1980s, continue to play. Also called complementary dna) is synthetic dna that has been transcribed from a specific mrna through a reaction using the enzyme reverse. Construction of cdna clones involves the synthesis of complementary dna. What Is Cdna Cloning.
From www.researchgate.net
Cloning Strategy to incorporate cDNA encoding ?secretase components What Is Cdna Cloning Cdna cloning is one of the fundamental technologies in molecular biology, and most of our knowledge about transcripts and proteins is. Unlike genomic dna clones, cdna clones lack intron sequences, making them the clones of choice for analyzing the protein product of a gene. Also called complementary dna) is synthetic dna that has been transcribed from a specific mrna through. What Is Cdna Cloning.
From www.slideshare.net
Approaches to cDNA Cloning and Analysis What Is Cdna Cloning Construction of cdna clones involves the synthesis of complementary dna from mrna and then. The cloning of expressed genes and the polymerase chain reaction (pcr), two biotechnological breakthroughs of the 1970s and 1980s, continue to play. Unlike genomic dna clones, cdna clones lack intron sequences, making them the clones of choice for analyzing the protein product of a gene. In. What Is Cdna Cloning.
From www.mun.ca
cDNA What Is Cdna Cloning Cdna cloning is one of the fundamental technologies in molecular biology, and most of our knowledge about transcripts and proteins is. Unlike genomic dna clones, cdna clones lack intron sequences, making them the clones of choice for analyzing the protein product of a gene. In molecular cloning, dna library construction refers to the creation of clones that carry dna fragments. What Is Cdna Cloning.
From www.weizmann.ac.il
DNA cloning The Dana and Yossie Hollander What Is Cdna Cloning Cdna clones are copies of mrnas. In molecular cloning, dna library construction refers to the creation of clones that carry dna fragments representing the complete genomic. Cdna cloning is one of the fundamental technologies in molecular biology, and most of our knowledge about transcripts and proteins is. Cdna (short for copy dna; Construction of cdna clones involves the synthesis of. What Is Cdna Cloning.
From www.onlinebiologynotes.com
cDNA cloning Principle and steps involved in cDNA cloning Online What Is Cdna Cloning Construction of cdna clones involves the synthesis of complementary dna from mrna and then. Cdna cloning is one of the fundamental technologies in molecular biology, and most of our knowledge about transcripts and proteins is. Cdna (short for copy dna; Unlike genomic dna clones, cdna clones lack intron sequences, making them the clones of choice for analyzing the protein product. What Is Cdna Cloning.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT DNA cloning technology PowerPoint Presentation ID What Is Cdna Cloning Cdna clones are copies of mrnas. Unlike genomic dna clones, cdna clones lack intron sequences, making them the clones of choice for analyzing the protein product of a gene. Also called complementary dna) is synthetic dna that has been transcribed from a specific mrna through a reaction using the enzyme reverse. Construction of cdna clones involves the synthesis of complementary. What Is Cdna Cloning.
From www.researchgate.net
Schematic representation of the construction of fulllength cDNA clone What Is Cdna Cloning Cdna (short for copy dna; Unlike genomic dna clones, cdna clones lack intron sequences, making them the clones of choice for analyzing the protein product of a gene. Construction of cdna clones involves the synthesis of complementary dna from mrna and then. In molecular cloning, dna library construction refers to the creation of clones that carry dna fragments representing the. What Is Cdna Cloning.
From www.slideshare.net
Approaches to cDNA Cloning and Analysis What Is Cdna Cloning Cdna cloning is one of the fundamental technologies in molecular biology, and most of our knowledge about transcripts and proteins is. Construction of cdna clones involves the synthesis of complementary dna from mrna and then. Unlike genomic dna clones, cdna clones lack intron sequences, making them the clones of choice for analyzing the protein product of a gene. The cloning. What Is Cdna Cloning.
From www.snapgene.com
The Plasmid Cloning Cycle Snapgene What Is Cdna Cloning The cloning of expressed genes and the polymerase chain reaction (pcr), two biotechnological breakthroughs of the 1970s and 1980s, continue to play. Also called complementary dna) is synthetic dna that has been transcribed from a specific mrna through a reaction using the enzyme reverse. Unlike genomic dna clones, cdna clones lack intron sequences, making them the clones of choice for. What Is Cdna Cloning.
From goldbio.com
Reverse Transcriptase & cDNA Overview & Applications GoldBio What Is Cdna Cloning Cdna clones are copies of mrnas. Construction of cdna clones involves the synthesis of complementary dna from mrna and then. In molecular cloning, dna library construction refers to the creation of clones that carry dna fragments representing the complete genomic. Unlike genomic dna clones, cdna clones lack intron sequences, making them the clones of choice for analyzing the protein product. What Is Cdna Cloning.
From pediaa.com
Difference Between DNA and cDNA Definition, Characteristics What Is Cdna Cloning Cdna clones are copies of mrnas. Unlike genomic dna clones, cdna clones lack intron sequences, making them the clones of choice for analyzing the protein product of a gene. Cdna cloning is one of the fundamental technologies in molecular biology, and most of our knowledge about transcripts and proteins is. Cdna (short for copy dna; Also called complementary dna) is. What Is Cdna Cloning.
From www.pinterest.co.uk
Poster cDNA library Definition and Steps in the construction of cDNA What Is Cdna Cloning The cloning of expressed genes and the polymerase chain reaction (pcr), two biotechnological breakthroughs of the 1970s and 1980s, continue to play. Unlike genomic dna clones, cdna clones lack intron sequences, making them the clones of choice for analyzing the protein product of a gene. Cdna clones are copies of mrnas. Also called complementary dna) is synthetic dna that has. What Is Cdna Cloning.
From www.thermofisher.com
Common Cloning Applications and Strategies Thermo Fisher Scientific UK What Is Cdna Cloning Cdna cloning is one of the fundamental technologies in molecular biology, and most of our knowledge about transcripts and proteins is. Construction of cdna clones involves the synthesis of complementary dna from mrna and then. In molecular cloning, dna library construction refers to the creation of clones that carry dna fragments representing the complete genomic. The cloning of expressed genes. What Is Cdna Cloning.
From www.researchgate.net
Schematic representation of the cDNA library construction method What Is Cdna Cloning Cdna (short for copy dna; The cloning of expressed genes and the polymerase chain reaction (pcr), two biotechnological breakthroughs of the 1970s and 1980s, continue to play. Unlike genomic dna clones, cdna clones lack intron sequences, making them the clones of choice for analyzing the protein product of a gene. Cdna clones are copies of mrnas. Cdna cloning is one. What Is Cdna Cloning.
From themedicalbiochemistrypage.org
Molecular Biology in Medicine The Medical Biochemistry Page What Is Cdna Cloning Cdna clones are copies of mrnas. Cdna cloning is one of the fundamental technologies in molecular biology, and most of our knowledge about transcripts and proteins is. Construction of cdna clones involves the synthesis of complementary dna from mrna and then. Cdna (short for copy dna; Unlike genomic dna clones, cdna clones lack intron sequences, making them the clones of. What Is Cdna Cloning.
From www.researchgate.net
Schematic representation of cloning fulllength CymMV cDNA clones What Is Cdna Cloning Cdna cloning is one of the fundamental technologies in molecular biology, and most of our knowledge about transcripts and proteins is. The cloning of expressed genes and the polymerase chain reaction (pcr), two biotechnological breakthroughs of the 1970s and 1980s, continue to play. Unlike genomic dna clones, cdna clones lack intron sequences, making them the clones of choice for analyzing. What Is Cdna Cloning.
From file.scirp.org
A method to synthesize cDNA constructs by homology based What Is Cdna Cloning Unlike genomic dna clones, cdna clones lack intron sequences, making them the clones of choice for analyzing the protein product of a gene. Construction of cdna clones involves the synthesis of complementary dna from mrna and then. Also called complementary dna) is synthetic dna that has been transcribed from a specific mrna through a reaction using the enzyme reverse. Cdna. What Is Cdna Cloning.